- What functions does the pancreas perform in our body?
- The most common causes of pancreatitis
- Signs of acute pancreatitis (PZT)
- Signs of chronic pancreatitis (PZT)
- What is the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases?
- How to treat the pancreas?
- Diet to treat pancreatic diseases
- Herbs for pancreas
- Pharmacological treatment of the pancreas
The pancreas performs important digestive and hormonal functions in our body, so when it fails, unpleasant ailments occur. Since untreated ones can cause serious complications, it is worth knowing how to recognize them and when to see a doctor. Below we explain the symptoms of pancreatitis, the most common condition of this organ, which usually affects people after 40 years of age. We also suggest how to treat the pancreas once it has been damaged and what is the relevance of the treatment to the right diet and herbs.
What functions does the pancreas perform in our body?
In man, the pancreas is an oblong organ (and exactly a gland) running across the upper abdominal cavity, roughly in the middle, between the spine and the stomach. There's a duodenum and spleen nearby. It has an elongated and irregular shape, and its length can be from a dozen to 20 cm. The location of the pancreas is worth knowing to properly recognize the symptoms of inflammation of this organ. This important gland consists of two parts responsible for different functions:
- is responsible for the production of hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which play a key role in regulating blood sugar,
- the external secretion part – participates in the digestion of foods by producing so-called pancreatic juice containing important digestive enzymes; it is introduced into the duodenum (including bile from the liver) to further digest the digestive pulp coming out of the stomach.

As you can see, the pancreas performs many important tasks in our body. Unfortunately, its damage and diseases such as inflammation have a negative effect on the work of both parts of it, i.e. hormonal and digestive functions.
The most common causes of pancreatitis
In most cases, treatment of the pancreas is necessary when inflammation occurs, as it is the most frequently diagnosed condition of this organ. It occurs in two forms – acute (OCT) and chronic (PCT). In both cases, you have to count on bad symptoms and long treatment, as we will write more below. The disease is mainly occurring in adults over 40 years of age and then the main factors behind it are:
- alcohol abuse (responsible for most cases of pancreatitis),
- gallstone
- abdominal injuries.
The risk of developing disease is increased in smokers, overuse of medicines such as NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, patients with certain diseases, such as chronic renal failure, or those on an abnormal diet (too fat and rich meals). Some cases of OZT or PZT are associated with viral infections and autoimmune diseases. Whatever the cause, the inflammation of the pancreas is due to excessive production of digestive enzymes, which penetrate the surrounding tissues and damage them. In extreme cases, this may result in a necrotic form of inflammation and even damage to adjacent organs. It is worth mentioning, by the way, that the third and more dangerous disease is pancreatic cancer, which occurs more frequently in men, usually reveals itself after the age of 60 and often does not give any symptoms for a very long time. Unfortunately, this causes late detection of the disease, which practically deprives the patient of a chance to heal.
Signs of acute pancreatitis (OCT) and treatment
The difference between acute and chronic pancreatitis concerns the duration and duration of the disease. Acute inflammation (ODT) occurs suddenly. It is manifested by a strong, bandaged and radiating upper abdominal pain. It may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, decreased intestinal peristalsis (displacement problems), and sometimes increased heart rate and low blood pressure. The patient’s abdomen is most commonly swollen (bloated) and shows pain when pressed with his fingers. The cause of these conditions is usually prolonged ingestion of excessive alcohol or gallstones. A pain attack that may indicate OZT requires urgent medical intervention. The patient usually needs to be hospitalised, and the treatment of the pancreas in this case usually involves the administration of painkillers and reducing the production of digestive juices. It is also important to supplement fluids and implement a light low-fat diet. If necessary, food is administered by parenteral route. In some situations, when, for example, necrotic lesions or bacterial infections occur, antibiotic therapy or even surgery is necessary to cut out an organ fragment.

Signs of chronic pancreatitis (PZT)
As the name suggests, a chronic strain of pancreatitis is a long-term condition. It involves appearing at different intervals of inflammation. As they lead to the gradual replacement of healthy tissue of the organ with fibrous tissue, the effect of the disease is its failure. The symptoms of PZT are only slightly different from the symptoms of acute inflammation and include mainly:
- recurrent abdominal pain of varying degrees, occurring most frequently after a meal and lasting on average several days (normally localized in the left upper abdominal cavity and can radiate to the spine),
- gradual weight loss despite good appetite,
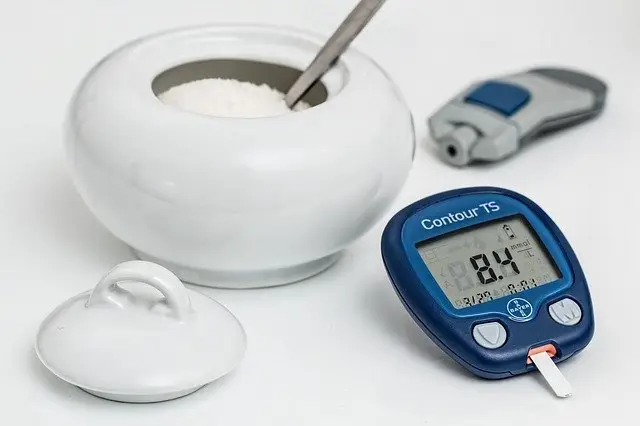
- problems with glucose tolerance, eventually even developing diabetes,
- itching,
- common fatty diarrhoea
- flatulence,
- vomiting,
- jaundice (e.g. slight yellowing of the eyes and skin).
As with acute inflammation, the underlying cause of the disease is alcohol abuse. Although in this case, poor diet, obesity and abuse of certain medicines are also important risk factors. The reason for the disease is much less often hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcaemia, or renal failure.
What is the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases?
Before treating the pancreas, the disease should be properly diagnosed. First of all, it is vital to be able to recognize and interpret the symptoms described above. The most important of these include abdominal pain, which in the case of pancreatic diseases is usually quite intense and located in a specific place, so it is difficult to miss. It should not be underestimated either, since if acute, particularly necrotic glanditis occurs, complications may be very serious, even of a systemic nature. For precise diagnosis of OZT or PZT, a detailed medical examination and a simple medical examination (e.g. abdominal palpation) is usually sufficient. Several additional specialised studies are sometimes required. These studies include:
- determination of pancreatic enzymes (lipases and amylases) in serum and urine (note: test results are not always conclusive, therefore they cannot be the basis for the final diagnosis),
- ultrasound (this is a basic study to diagnose PZT and its cause, e.g. gallstone),
- abdominal CT,
- ECPW, the so-called retroscopic endoscopic chalongiography, is an invasive study and is therefore conducted in exceptional situations and only in hospital conditions,
Complementary tests are sometimes recommended, e.g. for OB and blood glucose, or liver tests, which can give a more complete picture of the patient’s health.
Your doctor will decide on these tests. It is worth remembering that although an enzyme test can be done on its own in an analytical laboratory (e.g. for the presence of amylase in urine), it is not appropriate to make a diagnosis on the basis of the result obtained. It is common that with pancreatitis the levels of enzymes are normal. In turn the increased presence of amylase in urine may also mean a completely different condition, e.g. problems with gallbladder, ovaries, kidneys and even lungs. Therefore, any disturbing symptoms of the pancreas should be consulted by your doctor.
How to treat the pancreas?
The appearance of symptoms of pancreatitis, even in mild form, requires appropriate treatment. Treatment should be adapted to the type and degree of disease progression. Unfortunately, if the inflammation is not autoimmune, the therapy is almost only symptomatic, which is to combat inflammation, pain and metabolic disorders associated with abnormal hormone secretion, e.g. insulin.
Among the most common treatments for pancreatic diseases are:
- diet,
- pharmacological medicines, including those with analgesic effects,
- if you develop diabetes,
- endoscopic procedures (e.g. removal of cysts or deposits or enlargement of the pancreas),
- surgery (used in severe cases where other therapeutic methods do not produce the expected result).
Diet and pharmacology play the most important role in the treatment of pancreas, especially in the case of diagnosed PZT.
-
 Żelki z grzybami TOPICAL – 30 szt58.00 zł
Żelki z grzybami TOPICAL – 30 szt58.00 zł -
 Żelki z melatoniną dla dzieci – 30 szt58.00 zł
Żelki z melatoniną dla dzieci – 30 szt58.00 zł -
Product in promotion
 Gift set Easter Basket IVThe original price was: 74.00 zł.69.00 złThe current price is: PLN 69.00.
Gift set Easter Basket IVThe original price was: 74.00 zł.69.00 złThe current price is: PLN 69.00. -
 KUDZU korzeń 420 mg – 90 kapsułek53.90 zł
KUDZU korzeń 420 mg – 90 kapsułek53.90 zł -
 GLUTATION – 90 kapsułek79.00 zł
GLUTATION – 90 kapsułek79.00 zł -
Product in promotion
 Easter Basket Gift Set IIIThe original price was: PLN 84.00.79.00 złThe current price is: 79.00 PLN.
Easter Basket Gift Set IIIThe original price was: PLN 84.00.79.00 złThe current price is: 79.00 PLN. -
Product in promotion
 Easter Basket Gift Set IIThe original price was: PLN 84.00.79.00 złThe current price is: 79.00 PLN.
Easter Basket Gift Set IIThe original price was: PLN 84.00.79.00 złThe current price is: 79.00 PLN. -
 SPERmidin++ 6 mg 90 capsules49.90 zł
SPERmidin++ 6 mg 90 capsules49.90 zł -
 Black BLOOD Syrup – 150ml9.90 zł
Black BLOOD Syrup – 150ml9.90 zł
Diet in treatment disease pancreas
It is worth knowing that a special diet is recommended both for patients suffering from chronic pancreatitis and for those who have had an acute attack of this disease. Nutrition rules should be determined on a case-by-case basis. After acute pancreatitis, special dietary recommendations should usually be followed for approximately 6 weeks. In the case of recurrent and chronic problems, a permanent change in eating habits is indicated.
Diet in pancreatic diseases is primarily low-fat and light-digestion, initially also with reduced protein. The basic dietary principle is total cessation of alcohol and cessation of smoking. It is also important to eat small meals at regular intervals – it should be about 4 or 5 during the day. The diet should not contain severe and fatty foods and those that may irritate the pancreas.
The following shall therefore be excluded:
- fried dishes and greasy sauces,
- fat meat, meats and fish,
- yellow cheese, mayonnaise, cream,
- butter, lard, margarine,
- cream cakes,
- bloating vegetables, e.g. cabbage, legumes, onions,
- too much raw fruit and vegetables,
- cereal products with a lot of fiber, e.g. groats, whole grain bread,
- spicy pepper spices, chilli,
- strong coffee and tea.
Pancreatitis menus should be dominated by cooked or baked dishes in foil. Additionally, lean meat (preferably poultry and veal), meats and dairy products with low fat content. It is also worth putting on delicate wheat bread, olive oil, puree soups, vegetables and cooked fruit, pasta, white rice, etc.

In chronic pancreatitis (PZT), patients often experience weight loss. Therefore, the diet should provide a sufficient number of calories per day. The menu is mainly based on protein and carbohydrates, but in the case of diabetes problems, it is necessary to avoid simple sugars, such as white sugars and sweets, but also honey, or sweet bananas and grapes.
In some cases, when a sick body causes a disturbance in the absorption of nutrients from food, vitamin preparations are necessary.
Herbs for pancreas
Herbotherapy is helpful in treating the pancreas, especially chronic diseases. The most recommended mixtures of herbs with a wide effect are: anti-inflammatory, accelerating the regeneration of the gland, or facilitating digestion by supporting the secretion of pancreatic enzymes. An example is the herb on the pancreas of Haim ( https://organis.pl/haima- pancreas-ecological- herb/) – this is a mixture of specially selected 4 natural herbs, which, through joint action, give excellent therapeutic effects. Their use is recommended during recovery after acute pancreatitis.and, as well as patients suffering from chronic diseases of varying degrees of severity.
The following herbs are included in the mixture:
- tatarak – its task is to stimulate bile secretion and digestive juices, as well as mucopolisaccharides protecting the mucosa of the stomach. It helps the digestive processes and relieves stomach problems. It is also effective with colic or flatulence. Additionally, the tatarac has antifungal and antibacterial effects,
- dandelion – used for any conditions associated with bile secretion. It stimulates the liver to secrete it, and by acting antispasmodicly, it facilitates its transport to the duodenum. In addition, the plant supports the production of gastric juices which also participate in the digestion process,
- sand mart – has a positive effect on the whole digestive system by relaxing its muscles. Improves digestion and runs wind-powered,
- nettle – helps purify the body from harmful metabolic products. It also helps to remove bile deposits from the digestive tract. At the same time, it stimulates the secretion of gastric juices, thereby improving liver function, pancreas and stomach, and thus digestive processes.

It is worth remembering that herbs, although available without a prescription, should not be used without prior consultation with a doctor, especially when taking any pharmacological remedies. It is especially dangerous to mix different species of herbs on your own – in this respect, it is safer to choose prepared mixtures that are developed by specialists.
Pharmacological pancreatic treatment
For the most commonly used medications for acute and chronic pancreatitis pain is due because the abdominal pain in these conditions is extremely severe for patients. However, popular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are not recommended to control it. They may exacerbate the disease. Usually, medicines from the group of so-called coanalgetics and optoids are prescribed.
As regards additional pharmacological measures, in some cases it is necessary to administer medicines that replace pancreatic enzymes to the patient when this body shows failure in this respect. Quite often patients also need to take vitamin supplements when using a low-fat diet. Some vitamins (e.g. A, D and E) are absorbed by the body by dissolving them in fat, the supply of which during the diet on the pancreas is too low.
All Signs of pancreatitis should never be ignored. Failure to take therapy can lead to serious complications. Most commonly these are cysts, necrosis, or fistulas pancreas, which often require surgical intervention. However, complications may also be systemic in nature, e.g., lead to diabetes, infection, kidney failure, duodenal stenosis, and pancreatic cancer. The risk of cancer affects especially people with PZT. Observing a proper diet and doctor's recommendations regarding e.g. total abstinence, as well as the use of supportive herbal therapy allows not only to ease the course of the disease but also to avoid serious complications.